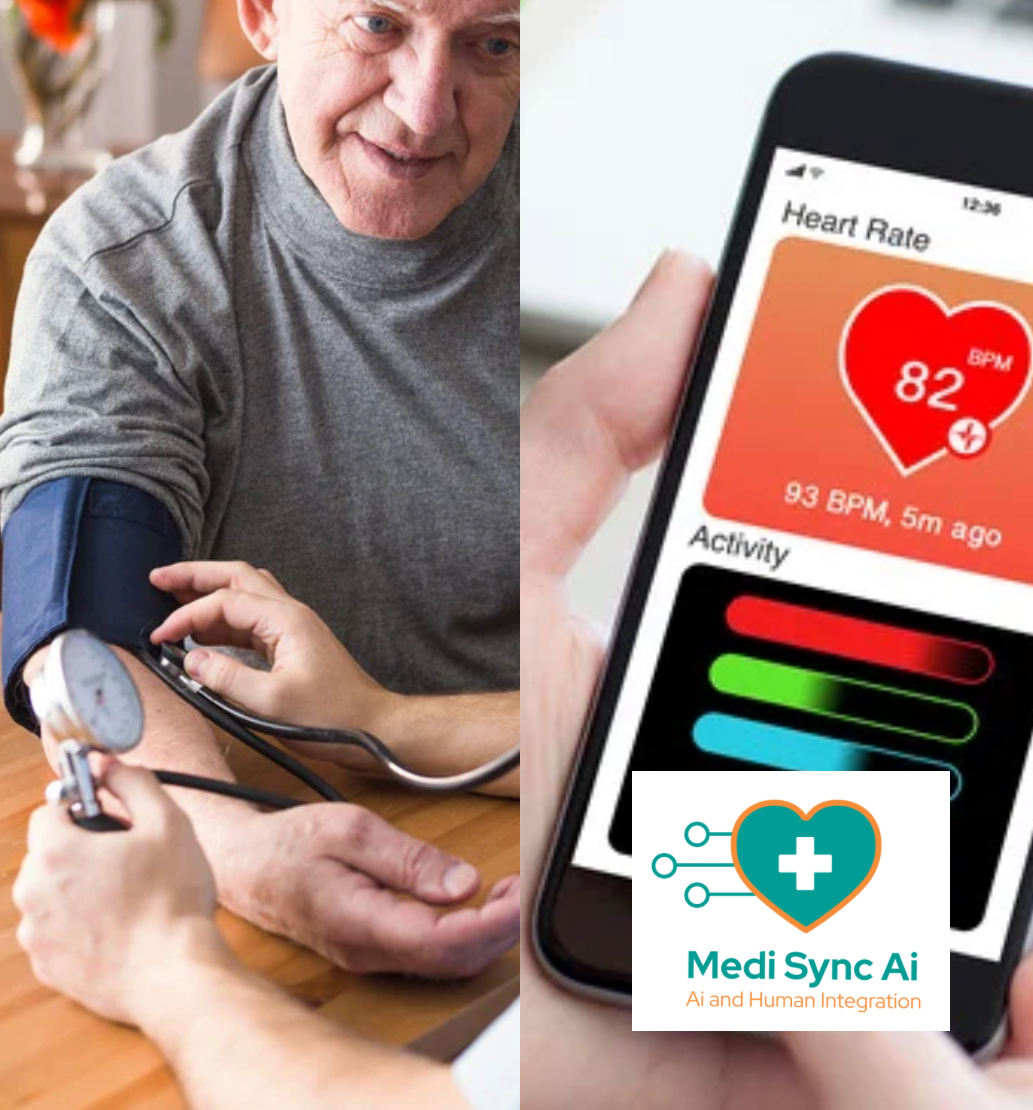
The integration of digital health solutions has transformed how healthcare providers monitor, diagnose, and manage patients remotely. Among the most widely used remote monitoring strategies today are Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM). While these two technologies share some similarities, they serve distinct purposes and are governed by different protocols.
Understanding the differences between RPM and RTM is critical for healthcare providers looking to optimize patient outcomes, enhance care efficiency, and maximize reimbursement opportunities. With chronic diseases affecting more than 60% of the U.S. population and a growing emphasis on value-based care, remote monitoring technologies have become essential tools in modern healthcare.
In this guide, we’ll explore the key differences between RPM and RTM, their benefits, and how they contribute to the evolving landscape of digital health. We’ll also look at future trends in remote monitoring and how providers can leverage these technologies effectively.
RPM vs. RTM – The Showdown: What is Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)?
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) is a digital health technology that enables healthcare providers to monitor patients’ physiological data outside traditional clinical settings. RPM devices collect real-time health metrics, such as:
• Blood pressure (e.g., for hypertension management)
• Blood glucose levels (e.g., for diabetes management)
• Heart rate and ECG readings (e.g., for cardiovascular conditions)
• Oxygen saturation (SpO2) (e.g., for respiratory diseases)
• Weight and fluid retention (e.g., for heart failure patients)
RPM is particularly beneficial for chronic disease management, allowing providers to track patients’ conditions continuously. This reduces hospital readmissions, improves patient adherence, and enhances clinical decision-making.
A key feature of RPM is automated data transmission—devices collect and send data directly to healthcare professionals via integrated electronic health record (EHR) systems, enabling timely interventions.
Example: A patient with congestive heart failure (CHF) using an RPM-enabled smart scale can have daily weight fluctuations monitored remotely. Sudden increases could indicate fluid retention, prompting early intervention before hospitalization is needed.
What is Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM)?
Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) is a relatively newer category of remote monitoring introduced by CMS in 2022 to expand digital care services. Unlike RPM, which primarily focuses on physiological data, RTM is designed to track non-physiological metrics related to therapy adherence and response.
RTM typically applies to patients undergoing:
• Musculoskeletal therapy (e.g., physical rehabilitation)
• Respiratory therapy (e.g., COPD management)
• Pain management programs
• Medication adherence monitoring
RTM relies more on patient-reported data, which can be collected via apps, wearable devices, or digital platforms. Patients often self-report therapy adherence, symptom progression, and treatment response, helping providers tailor interventions.
Example: A physical therapy patient recovering from knee surgery uses an RTM-enabled mobile app to log daily pain levels and exercise adherence. This data allows the therapist to adjust the rehab plan accordingly.
Key Differences Between RPM and RTM
| Feature | Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) | Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM) |
| Data Type | Physiological (objective) data (e.g., BP, heart rate) | Non-physiological (subjective) data (e.g., pain levels, therapy adherence) |
| Collection Method | Automated digital device transmission | Patient-reported via apps or software |
| Common Use Cases | Chronic disease management (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, CHF) | Musculoskeletal, respiratory therapy, pain management |
| Device Requirement | Requires FDA-approved medical devices | Does not require FDA-approved devices |
| Billing Eligibility | Billed by physicians, PAs, and nurse practitioners | Billed by broader providers, including therapists |
Understanding these key distinctions is crucial for healthcare organizations deciding which monitoring solution to implement based on their patient population and clinical objectives.
Benefits of RPM & RTM: Advantages of Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
1.Proactive Chronic Disease Management
• Early detection of health deterioration prevents complications.
• Reduces hospitalizations and emergency room visits.
2.Improved Patient Adherence & Engagement
• RPM devices send real-time alerts to patients and providers.
• Encourages patients to stay on top of medication and lifestyle changes.
3.Data-Driven Clinical Decision Making
• Continuous data helps predict risk trends for early interventions.
• Physicians can adjust treatment plans remotely based on insights.
4.Better Reimbursement & Revenue Opportunities
• RPM is reimbursable under CPT codes 99453, 99454, 99457, and 99458.
• Providers can earn up to $120 per patient per month with compliant RPM use.
Advantages of Remote Therapeutic Monitoring (RTM)
1.Enhances Physical Therapy & Rehabilitation
• Helps physical therapists track patients’ adherence to rehab programs.
• Supports pain management strategies with objective progress tracking.
2.Supports Behavioral Health & Medication Compliance
• Tracks therapy engagement for patients with mental health conditions.
• Monitors medication adherence, reducing prescription misuse risks.
3.Expands Digital Health Access
• RTM allows for non-physician provider billing, increasing flexibility.
• Supports care for diverse populations, including elderly patients.
4.CMS Reimbursement & Billing Flexibility
• RTM uses CPT codes 98975, 98976, 98977, and 98980.
• Can be billed by therapists, nurses, and other non-physician specialists.
Key Insight: Healthcare providers using both RPM and RTM can maximize patient coverage while increasing revenue potential through comprehensive remote monitoring services.
Future Trends in RPM and RTM
As digital health advances, RPM and RTM will continue evolving, integrating more AI-driven analytics, machine learning, and automation. Here are some key trends shaping the future:
1. AI-Powered Predictive Analytics
• AI algorithms will analyze large datasets from RPM and RTM to predict disease progression.
• Providers will receive automated risk scores for proactive interventions.
2. Expansion of Wearable Health Tech
• Next-gen wearable biosensors will provide continuous monitoring without user intervention.
• Smart clothing and implantable sensors may expand RPM applications.
3. Telehealth & Remote Monitoring Integration
• Telemedicine platforms will seamlessly incorporate RPM and RTM data, enhancing virtual care.
• EHR interoperability will improve data-sharing across provider networks.
4. Policy & Reimbursement Evolution
• CMS may expand reimbursement policies to further encourage RPM and RTM adoption.
• Private insurers are also beginning to recognize RTM for reimbursement.
5. Increased Focus on Home-Based Care Models
• With value-based care models gaining traction, home-based RPM/RTM solutions will become a primary strategy for chronic disease management.
Industry Insight: By 2027, the global RPM market is expected to exceed $175 billion, signaling its long-term impact on healthcare. (Source: Global Market Insights)
Remote monitoring technologies like RPM and RTM are revolutionizing patient care, providing healthcare professionals with real-time data to enhance decision-making, reduce hospitalizations, and improve patient adherence.
While RPM focuses on physiological data collection, RTM expands into therapy monitoring, making both complementary solutions in modern healthcare. As AI, wearables, and telehealth continue evolving, integrating both RPM and RTM will be key to delivering comprehensive, data-driven patient care.
Healthcare organizations that invest in RPM and RTM now will be better positioned for future advancements, benefiting from improved patient outcomes, streamlined workflows, and enhanced revenue opportunities.
Take the Next Step with MediSyncAI
MediSyncAI offers cutting-edge AI-powered remote monitoring solutions designed to help providers scale RPM and RTM efficiently. Our platform enables:
✅ Seamless EHR Integration
✅ Automated Data Insights
✅ HIPAA-Compliant Remote Monitoring
✅ Optimized Reimbursement Tracking
Contact us today to discover how MediSyncAI can help you maximize the impact of RPM & RTM in your practice!